Manage Conductor organizations
An organization is the main Conductor entity under where Kubernetes clusters are onboarded. It captures the details around your Free or Enterprise plan, and tracks the resources and limits assigned to that organization.
👥User access
Invite administrators, editors, and viewers, and scope permissions to individual clusters.
Manage users →🔑Automation
Use API keys to authenticate via non-interactive automation through the Diagrid CLI.
Work with API keys →🪪Single sign-on
Connect your SAML 2.0 identity provider so employees can log in with delegated credentials.
Configure SSO →📝Audit logs
Track create, update, and delete operations for clusters, rollouts, alerts, channels, users, and API keys.
Review audit history →Adding users, configuring SSO, generating API keys, and viewing audit logs are only available in Conductor Enterprise.
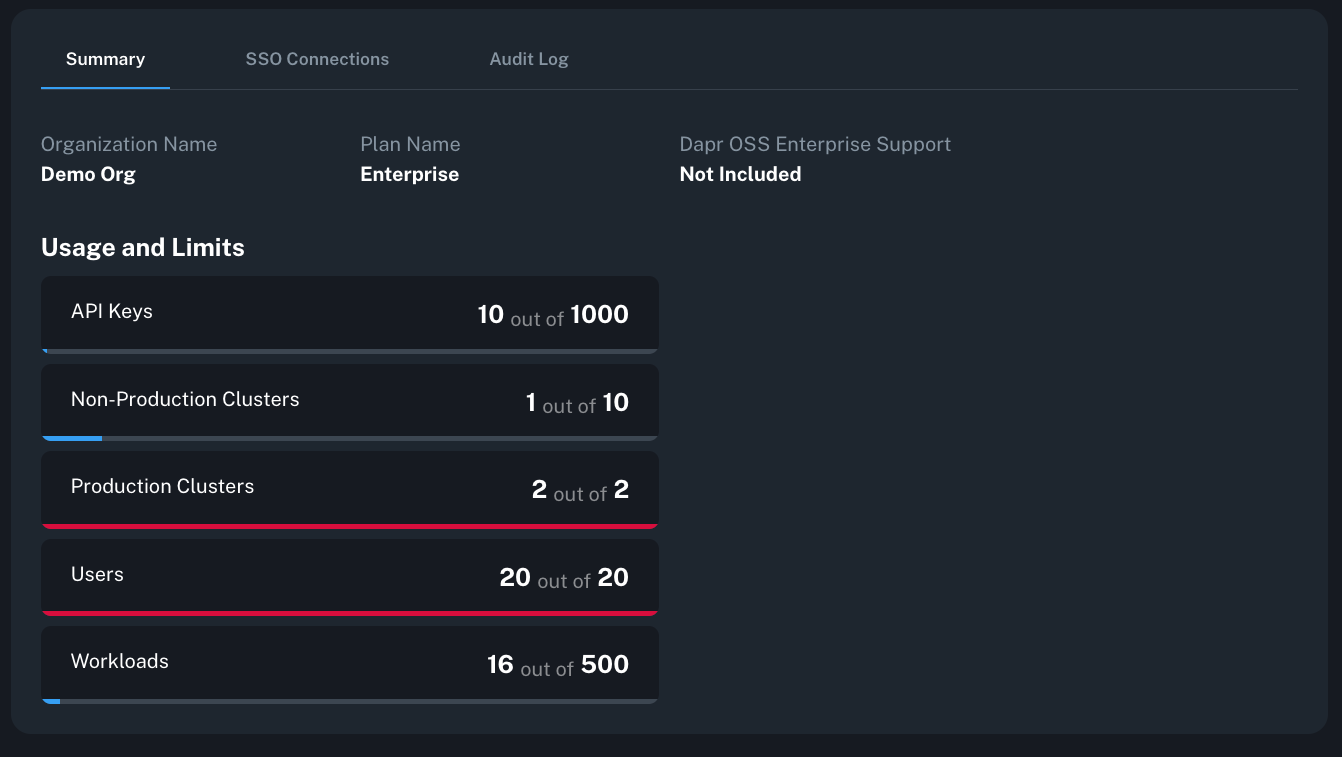
Understand organization usage
The organization dashboard surfaces your current usage and entitlements so you can see how many clusters you have onboarded, your plan and organization ID, and how close you are to plan limits.
Manage users and roles
Administrators invite users and assign roles that apply to every cluster or to specific cluster scopes.
Invite new users
Use the Diagrid CLI to invite new users:
diagrid product use conductor
# Example: invite an admin
diagrid user create --email user@gmail.com --name user --role diagrid:admin
Invite users from the console
- In the Conductor console sidebar, open Users.
- Select + Add User and enter the user's name and email (email cannot be edited later).
- Choose one or more roles. See Role definitions.
- Select Create to send the invitation.
If SSO is enabled, you are required to invite users via Conductor in addition to inviting them with your IdP.
Role definitions
- Viewer – Read-only access to clusters, applications, notifications, advisor, alerts, notification channels, and agent logs. No organization, user, or API key management.
- Editor – Viewer access plus the ability to manage cluster connections, manifests, Dapr configs and upgrades, application rollouts, and API keys. Cannot edit organization or user settings. Scoped editor roles limit these capabilities to selected clusters.
- Admin – Editor access plus organization settings, user invites/removals, role management, and password resets. Admin roles are global; scoping does not add value.
Automate operations with API keys
API keys are named tokens with role assignments used for authenticating automation via the Diagrid CLI. After creation, include the token value with the --api-key flag to run commands under that key's permissions. Store the secret safely, for example:
conductor_api_key=$(cat /secure-folder/diagrid-secret-token)
diagrid clusters list --api-key "${conductor_api_key}"
Refer to the Diagrid CLI reference for additional commands that accept the --api-key flag.
API key secrets are only shown during creation. Copy the token before closing the dialog.
Generate API keys
Create API keys using the Diagrid CLI using the following reference. API responses include the secret token so make sure to copy it immediately because it is only displayed once.
- Global role format:
diagrid:<role>(admin,editor, orviewer) - Scoped role format:
diagrid:<role>:clusters:<clusterIds>where<clusterIds>is comma-separated
# Global admin key that expires in 24h (86400 seconds)
diagrid apikeys create --name my-api-key --role diagrid:admin --duration 86400
# Scoped editor key for one cluster, expires in 30 days (2,592,000 seconds)
cluster_id=$(diagrid clusters list | jq -r '.[0].id')
diagrid apikeys create \
--name my-cluster-editor \
--role diagrid:editor:clusters:${cluster_id} \
--duration 2592000
Create API keys from the console
- In the console sidebar, open API Keys.
- Select + Create API Key and provide a unique name.
- Choose an expiration period (avoid
neverunless required). - Assign roles. See Role definitions.
- Select Create, then copy and securely store the token.
Delete API keys
Delete API keys using the Diagrid CLI:
# Find the key ID
diagrid apikeys list
# Delete by ID
diagrid apikeys delete <my-api-key-id>
Delete API keys from the console
- In the console sidebar, open API Keys.
- Locate the key to remove and open the action menu (three dots).
- Select Delete API Key and confirm.
SSO authentication
Single sign-on (SSO) lets Conductor users authenticate through their own SAML 2.0 identity provider (IdP). Native Conductor logins remain available, but every SSO user must still be invited to the organization or their IdP or the session will be rejected. Email addresses that match the configured login domain are routed through SSO automatically while other domains continue to use the native flow.
Single sign-on is available to Conductor Enterprise customers only.
Configure SSO
Prepare the domain
Contact your Diagrid Customer Success representative with the email domain you want to enforce so it can be allowlisted.
Gather IdP values
Capture the inputs Conductor requires:
- Connection type:
SAML 2.0 (samlp) - Name: Descriptive label for the connection
- Email domain: Domain that enforces SSO (for example,
@email.com) - Sign-in endpoint: IdP login URL
- Sign-out endpoint (optional): IdP logout URL for single logout (SLO)
- Signing certificate file: IdP certificate (
.ceror.pem)
Configure Conductor and your IdP
Paste the required values into Conductor, then copy the generated Callback URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) and Entity ID back into your IdP.
Okta requirement: Okta SAML configurations must include the user.email attribute in the Attribute Statements list or login fails.
Test the connection
Save your changes and sign in from a private browser session at https://conductor.r1.diagrid.io/. The first successful login always performs two attempts and shows a requires_login_again message—this is expected and should not happen after the first login.
Audit logging
Conductor records create, update, and delete operations for clusters, application rollouts, alerts, channels, users, and API keys. The past 30 days of activity are available to users with the Admin role under the Organization -> Audit Log page.
You can filter the audit log by:
- Event name – The type of operation that was executed (create, update, delete, and so on).
- Log type – The resource category affected by the operation.
- User – The email of the user who triggered the operation, or blank if an API key made the change.
- Account type – Whether the change originated from a user session or an API key.