Components
Dapr components connect applications to underlying infrastructure resources via the Dapr Building Block APIs. Conductor provides visibility into all Dapr components deployed on a connected Kubernetes cluster.
For every component, core details are organized by columns Name, Namespace, Type, Version, and Scoped Apps.
In addition, the component is assigned an Initialization Status which provides an easy way for users to catch potential component configuration errors. The section below covers this concept in more detail.
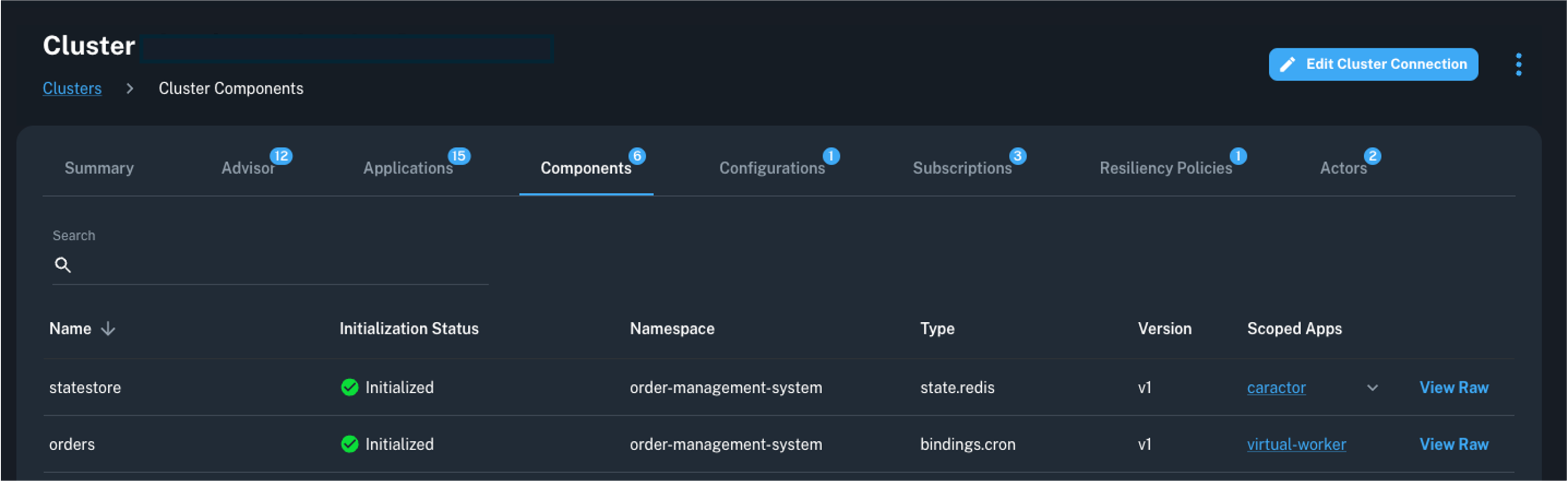
Component Initialization
Dapr component initialization runs on a minute-by-minute basis to ensure all components running in a cluster are configured correctly before being loaded by Dapr-enabled applications. The component initialization is comprised of the following steps:
- The Conductor agent retrieves a list of all Dapr resources of kind
Componentacross namespaces in the cluster. - A programmatically instantiated version of each component is created inside the Conductor agent, where its metadata fields are applied and the associated component's implementation
Init()function is executed. This result is then reported back to Diagrid Cloud. - The result is shown in the Conductor console in the Initialization Status column of both the Cluster and App Components lists. A green checkmark is displayed when the component has been initialized successfully, and a red icon for an error, along with the error message and timestamp from the last time the error occurred. This result can also be seen in each component's manifest in the
initStatusfield by clicking on View Raw. The absence of theinitStatusfield indicates that the component was initialized successfully.
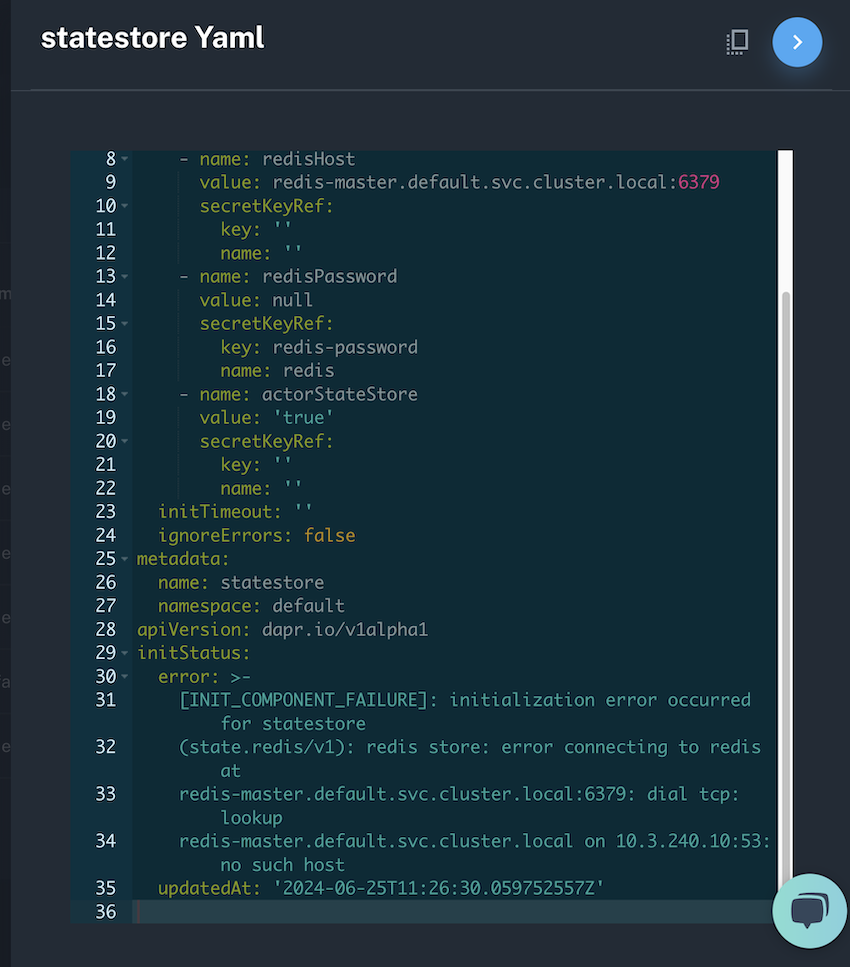
Here is an example of a component that failed to initialize:
Disabling Initialization
The section after this describes a few known limitations to component initialization checks. A component affected by any of these scenarios is not guaranteed to have an accurate Initialization Status. However, the initialization can be disabled Cluster-wide, or effectively disabled (with component type checks only) on a Per-Component basis.
Cluster-wide
Component initialization needs cluster-wide read access to components and secrets in order to properly validate across all namespaces and with resolved secrets. By disabling the feature, the agent can restrict these permissions to only the dapr and agent namespaces. This is described further within the RBAC permissions section.
To disable component initialization cluster-wide for a Helm-managed agent, set the value agent.enableComponentValidation to false in your Helm configuration.
This helm value ultimately passes the argument --componentinit.enabled=<true/false> to the agent deployment. So, on a normal, manifest-backed agent, this argument can be used directly, but without permissions reduction benefits the Helm Managed mode has.
Per-Component
By adding the diagrid.io/component-init-type-only: "true" annotation to a component, initialization will only check to see that the component's type is supported by Dapr. Here is an example component definition with this annotation:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: statestore
annotations:
diagrid.io/component-init-type-only: "true"
spec:
type: state.redis
version: v1
metadata:
- name: redisHost
value: localhost:6379
- name: redisPassword
value: ""
Because diagrid.io/component-init-type-only: "true" is present, initialization is reduced to only perform a check on type: state.redis.
The example component passes as written above, but would fail if its type was invalid, such as type: state.rwwdis.
Known Limitations
Unsupported Components
For security reasons, the agent doesn't have access to the application container. This means the following components cannot be validated and will always appear initialized successfully: bindings.localstorage, secretstores.local.env, secretstores.local.file
Pod-Identity Enabled Components
Dapr components that use pod identity mechanisms such as Azure Active Directory Workload Identity or IAM Roles for pods with a Kubernetes service account will always fail to be initialized due to lack of permissions on the Conductor agent pod to authenticate with the identity provider and validate the component.
Cross-Namespace Component Checks
Some components that reside in a different namespace than the Conductor agent have dependencies that can lead to false communication errors, when in fact the component is healthy in its own namespace. Kubernetes network policies between namespaces can also cause incorrect component initialization statuses.
For example:
Let's say a Dapr-enabled app that uses the following MongoDB component is deployed in the namespace crud-app. The MongoDB server has a hostname mongo-mongodb, and is deployed with a Kubernetes Service in the same crud-app namespace:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: mongo-statestore
namespace: crud-app
spec:
type: state.mongodb
version: v1
metadata:
- name: host
value: mongo-mongodb:27017
Because the Conductor agent is running in the diagrid-cloud namespace, when the component's Init() function runs, it will attempt to connect to hostname mongo-mongodb:27017. Since this hostname does not resolve in the diagrid-cloud namespace, Init() will result in a communication error.
For the agent to check the component initialization status successfully, it's suggested to specify the service's name along with its corresponding namespace in the connection details like mongo-mongodb.crud-app:27017, or use the full hostname like mongo-mongodb.crud-app.svc.cluster.local:27017.
The following components do not abide by the above limitations and will always be validated successfully without the namespace constraints:
pubsub.redisstate.redisbindings.redisconfiguration.redisbindings.zeebe.jobworkerbindings.zeebe.commandbindings.httppubsub.kafkabindings.kafkapubsub.snssqs